Table of Content
- What is Laser Technology?
- Laser Technology Applications
- Laser Technology Challenges
- Why Choose Laser Technologies?
- Conclusion
In today's technological landscape, laser technology stands at the core of industrial development. This technology has a wide range of applications, from precision cutting to engraving. However, various applications of laser technology also present unique challenges, such as safety concerns and environmental impact.
What is Laser Technology?
Laser technology involves using light to perform various functions like cutting, engraving, measuring, and communication. The word "laser" stands for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Simply put, lasers produce highly focused beams of light that are coherent, monochromatic, and collimated.
Lasers are different from regular light sources so that they concentrate light into a powerful beam, enabling applications requiring precision and high energy density. This makes laser technology incredibly versatile across many industries. What are the uses of laser? Laser-cutting equipment is commonly used in manufacturing processes with high precision and speed.
Laser Technology Applications
What are the applications of lasers? There are applications of laser in various fields and across a diverse range of industries. Below, we explore some of the primary areas where laser solutions are transforming businesses.
1. Laser Cutting

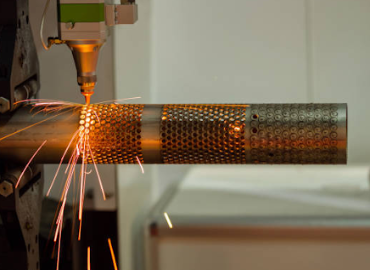
Laser cutting is one of the most common uses of laser technology. It involves using a high-powered laser beam to cut through various materials, including metals, plastics, wood, and ceramics. Laser cutting machine is valued for its ability to create intricate designs.
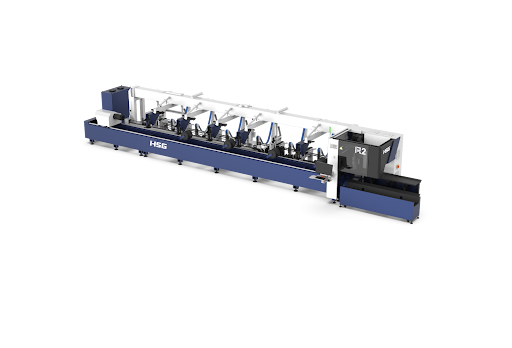
Laser Technologies provides advanced tube Laser Cutting Machines that offer accuracy for industries needing high-quality, complex tube cuts. The Universal Tube Laser Cutting Machine R2 is an advanced machine for businesses looking to cut various tubes and profiles efficiently. Tiny Tube Laser Cutting Machine R1 is a more compact and specialized version for smaller tubes. R1 is a precision micro-cutting machine that is space-efficient, easy to maintain, and ideal for small workshops or operations with limited space.
2. Laser Welding

Laser welding is a high-precision technique used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. What are the characteristics of a laser? Lasers provide a focused, intense heat source, which enables highly accurate welding without affecting surrounding materials. Laser Welding is particularly useful in applications where a high-quality, clean weld is needed or where the components being joined are delicate.
Smartweld is a handheld, cost-effective welding system with faster writing speed, making it easy to operate and saving welders annually, resulting in smoother welding seams. This machine is suitable for basic applications of laser in industry to the most advanced applications of laser in manufacturing.
3. Laser Engraving and Marking
Laser engraving and marking are used for permanent designs, logos, or text onto products. This is commonly used for industrial branding, product identification, and consumer personalization. The beauty of laser engraving is that it doesn’t require physical contact, meaning there's no wear on the material surface during the process, and the designs are highly durable.
Fiber Laser Marking Machines offer efficient, precise solutions for various materials, utilizing advanced fiber laser technology and beam control for high performance.
Laser Technology Challenges
Despite its many laser technology applications, laser cutting machines in India do come with certain challenges. Some of the major laser technology challenges include:
1. High Initial Investment
Laser systems, especially industrial machines, can have a high upfront cost. This can make them prohibitive for small businesses or startups. However, the long-term benefits of improved precision and efficiency often outweigh the initial investment.
2. Material Limitations
While lasers are highly effective for cutting a range of materials, not all materials are suitable for laser cutting. Reflective materials like copper and brass can cause laser beams to scatter, reducing cutting efficiency. However, technological advancements are continually expanding the materials that can be processed with lasers.
3. Training and Expertise
Laser machines often require specialized knowledge to operate effectively. Operators need to be trained in how to handle the equipment, maintain it, and troubleshoot any issues that may arise. Companies must invest in training to ensure that their staff can utilize the full potential of laser technology.
4. Safety Concerns
Lasers emit powerful beams of light that can cause harm if not handled properly. Protective measures such as shields, and proper machine enclosures are necessary to ensure the safety of workers. Manufacturers must adhere to stringent safety standards to prevent accidents.
5. Maintenance and Calibration
Like all high-tech equipment, laser systems require regular maintenance and calibration to maintain their performance and precision. Although maintenance schedules can be planned, machine downtime can still be disruptive, particularly in high-demand operations.
Why Choose Laser Technologies?
Laser Technologies stands as a reliable partner for businesses looking to integrate laser-cutting solutions into their operations. With a focus on quality, innovation, and customer satisfaction, Laser Technologies provides products that address the needs of modern manufacturing industries.
1. Innovative Solutions
Laser Technologies offers innovative machines such as the universal tube laser cutting machine R2 and the tiny tube laser cutting machine R1, both of which are designed to meet the demands of industries requiring high-precision cutting. These machines provide versatile, reliable, and efficient solutions for tube processing, ensuring that customers receive the best-in-class technology.
2. Superior After-Sales Support
It is committed to ensuring that customers get the most out of their laser machines. Their dedicated after-sales support team provides technical assistance, troubleshooting, and maintenance services to keep your machines running at peak performance. Whether it’s machine installation, training, or regular servicing, Laser Technologies ensures that every customer gets the full value from their investment.
3. Customisation and Flexibility
Laser Technologies understands that different industries have unique needs. They offer customizable laser-cutting solutions that can be tailored to specific requirements. Whether you’re cutting small or large tubes or need specialized configurations, Laser Technologies works closely with customers to provide personalized solutions.
Conclusion
Laser technology has multiple industries, from precision cutting and applications. Laser-cutting machines like those offered by Laser Technologies provide businesses with the tools they need to stay ahead in the competitive manufacturing landscape. By choosing Laser Technologies the customers gain reliable support that ensures their machines perform at their best over the long term.